Calculate the volume of the Cylinder, surface area of the Cylinder and know the formulas.
Cylinder Calculator
Result:
| Radius: | 0 |
| Height: | 0 |
| Volume: | 0 |
| Surface Area: | 0 |
What is a Cylinder?
A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape which consists of two parallel circular bases separated by a distance. The circular cases are joined by a curved surface at a fixed distance from their centres. The centres of the two circular bases are connected by a line which is called the axis of the cylinder.
The figure below shows a cylinder.

In this figure, the two circular bases have the same radius r. They are separated by a distance h. This is known as the height of the cylinder. The cylinder has a curved surface which connects the two circular bases. Unlike cubes, cuboids and cones, a cylinder does not have any vertices. Because it has a curved surface, a cylinder is not a polyhedron.
Properties of Cylinder
Given below are some properties of a Cylinder.
Volume – This is the total space occupied by the cylinder.
Lateral surface area – The lateral surface area of a cylinder is the area of the cylinder excluding the surface area of the base. It only includes the area between the two bases.
Surface area – Surface area is the total area covered by the cylinder. It is equal to the sum of the lateral surface area and the area covered by the circular bases.
Cylinder formulas
Given below are the formulas of a cylinder.
| Volume | $$ πr^2h \;cubic \,units $$ |
| Lateral surface area | $$ 2πrh \;square \;units \;$$ |
| Surface area | $$ 2πr(r+h) \; square \;units \;$$ |
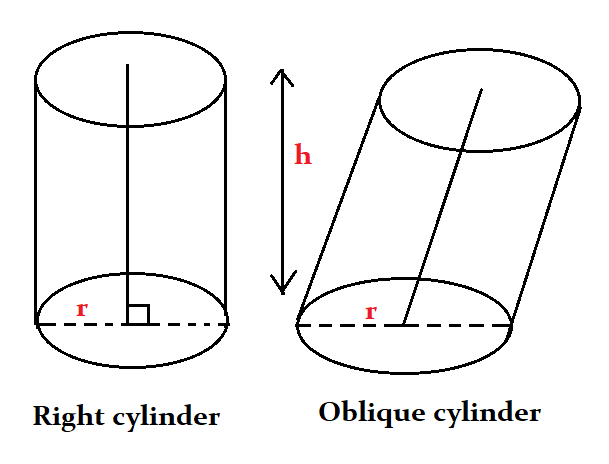
Characteristics of a Cylinder
Given below are the main characteristics of a cylinder.
The figure below shows the two main types of cylinders.
Areas of application
The most common example of a cylinder is the LPG gas cylinder used for cooking in almost every household. Tree trunks are also cylindrical in shape. Cylinders can also be seen in vehicles, such as the ignition cylinder for instance.
Some other examples of cylinders in everyday life are coffee cans, drink cans, food tins, candles, cups and mugs, toilet paper rolls, flower vases, aerosol cans, fire extinguishers, salt and pepper shakers, pencil holders and thermos flasks, to name a few. Some other examples are test tubes, lipstick containers, water tanks, toothpick holders and petroleum jelly containers. The amount of substance occupied by each of these everyday objects can be found quite easily by computing the volume.
We now consider a real-life example making use of the cylinder formulas.
Question: A farmer wishes to buy a new water tank for his farm because he needs more water for his crops. His current tank is a right circular cylinder which 6 m wide and has a height of 5 m. When he goes to the store, he has two options of tanks he could purchase.
If both the tanks cost the same, which tank should he buy?
Answer: The farmer currently owns a water tank which is 6 m wide and 5 m high. This would mean that the diameter of the base of the cylindrical tank is 6 m, and hence the radius is 3 m.
Volume of the present cylindrical tank = πr2 h m3 = π(3)2 5 m3 = 141.37 m3
At the store, the farmer has a choice of two tanks. For the first tank, the height is twice the height of the present one but the width is the same. So, h = 10 m, and r = 3 m.
Therefore, the volume of the first tank = π(3)2 10 m3 = 282.74 m3
For the second tank, the width is twice that of the present one, and the height is the same. Hence, h = 5 m, and r = 6 m.
Therefore, the volume of the second tank = π(6)2 5 m3 = 585.49 m3
Clearly, the tank which is twice as wide as the present water tank has a greater volume, than the tank with twice the height.
Since both tanks cost the same, the farmer should buy the second tank.

