Calculate the subtraction of two numbers:
Subtraction Calculator
Result:
| X - Y: | 0 |
What is Subtraction?
Subtraction is one of the basic arithmetic operations. It involves taking two numbers, and finding the difference between them. When we subtract one number from the other, we remove the smaller number from the bigger one. Subtraction is the inverse of addition. The symbol used to denote subtraction is “ - ”, called the minus sign. The subtraction process goes from right to left. We start from the ones place, then tens, then hundreds, and this goes on towards the higher digit places.
The number which is obtained after subtraction is called the difference of the two numbers. The number which is being subtracted is called the subtrahend, and the number which is being subtracted from is called the minuend. For example, consider “18 - 7 = 9”. Here, 18 is the minuend, 7 is the subtrahend, + is the subtraction operator and 9 is the difference.
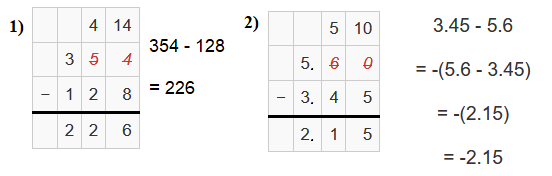
If the minuend is greater than the subtrahend, the subtraction process is quite straightforward. If the minuend is lesser than the subtrahend, we need to borrow a digit from the next higher digit of the minuend and then continue the subtraction process.
Properties of Subtraction
Given below are some important properties of subtraction.
Minuend – The number which is to be subtracted from.
Subtrahend – The number which is being subtracted.
Difference – The number obtained after the subtraction of two numbers.
Minus – Denoted by “ - ”, this sign is an arithmetic operator which indicates the subtraction of two or more numbers.
Closure property – When one number is subtracted from the other, the difference is not always a whole number. This means that, the number obtained after subtraction of two numbers may or may not be a whole number. So, the closure property is not followed for whole numbers. For example, 4 - 5 = -1. Here, 4 and 5 are whole numbers. Their difference, -1 is not a whole number.
The closure property holds if we consider the numbers as integers or real numbers. In this example, 4, 5 and -1 are integers, as well as real numbers. So, the subtraction of integers or real numbers follows the closure property.
Non-commutative property – Subtraction of two numbers is not commutative. When the order of the minuend and subtrahend are changed, the difference also changes. For example, 4 - 5 = -1 , but 5 - 4 = 1. Here, 4 - 5 ≠ 5 – 4. We obtain two different numbers when the order the numbers are altered.
Non-associative property – When the groups of numbers to be subtracted, are changed, the difference also changes. For example, (13 - 6) - 8 = -1 and 13 - (6 - 8) = 15. In the case of (13 - 6) – 8, we subtract 6 from 13 first to get 7, and then subtract 8 from 7 to get -1. In the second case, 8 is subtracted from 6 to get -2, which in turn gets subtracted from 13, to give 15 as the final answer. Hence, (13 - 6) – 8 ≠ 13 – (6 – 8).
Even if the numbers involved in the subtraction process are the same, the grouping of numbers is important. We cannot group any two numbers and subtract them.
Identity property – When 0 is subtracted from any number, we get that number itself. For example, 4 - 0 = 4.
Subtraction Rules
Below are the rules followed for the subtraction of numbers.
If the minuend is larger than the subtrahend, then subtraction will result in a positive number. For example, 8 - 5 = 3.
If the minuend is smaller than the subtrahend, then subtraction will result in a negative number. For example, 4 - 5 = -1.
If the subtrahend is a negative number, and the minuend is positive, then the negative signs cancel out and create a plus. In other words, this has the effect of adding the positive counterpart of the subtrahend to the minuend. For example, 8 – (-3) = 8 + 3 = 11.
If both the minuend and subtrahend are negative, the sign of the difference will be the sign of the larger of the two numbers. For example, - 8 – (- 3) = - 8 + 3 = -5. Whereas, - 8 – (- 20) = - 8 + 20 = 12.
Steps for subtraction
Subtraction of numbers can be done in the following steps.
The examples below demonstrate subtraction.
Areas of application
Given below are some examples of subtraction in everyday life.
Please check our interactive Subtraction table and learn further here

